EB-1 Green Card – High Salary or Remuneration
EB1 – High Salary or Remuneration
Secure Your EB-1 Green Card: Using High Earnings to Command U.S. Residency
Welcome to the Law Offices of Chris M. Ingram’s EB-1 Green Card series! We are thrilled to guide top earners toward permanent U.S. residency through the “High Salary” regulatory category.
If you command a significantly high salary in relation to others in your field, you may already satisfy one of the most powerful criteria for the EB-1 visa. This guide will explain exactly how to define “high salary,” how to prove it, and how to use official government data to validate your elite status.
The “High Salary” Criterion Defined
Per federal regulation 8 C.F.R. 204.5(h)(3)(ix), this category demands evidence that you have commanded a salary or other significantly high remuneration for services. Specifically, we must prove that your earnings place you in the top 10% (90th percentile) of professionals in your field.
Meeting this threshold is a strong signal to U.S. Immigration (USCIS) that there is exceptional demand for your specific skills and that you have risen to the very top of your endeavor.
Proving Your Earnings
Documentation is key. The evidence required changes slightly depending on where you are currently employed:
- For U.S. Workers: You should submit W-2 forms that reflect your total compensation. It is vital to include evidence of bonuses, commissions, and other taxable perks to verify your total earnings.
- For Non-U.S. Workers: You must provide tax returns or similar official government documents from your home country.
- Alternative Remuneration: If your compensation includes stock options, equity, or other non-cash perks, letters from a certified accountant can help validate the monetary value of these assets.
How to Verify Top-Tier Status Using O*NET Online
To prove you are in the top 10%, we need an objective benchmark. We utilize O*NET Online, a primary source of occupational information sponsored by the U.S. Department of Labor, alongside data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
Below is a step-by-step guide on how to analyze your occupation using these tools.
Example 1: Defining the Occupation (Computer Systems Analyst)
First, navigate to O*NET Online. You will see an “Occupation Keyword Search” field where you can search for almost any mainstream occupation.
For this example, we enter “Computer Systems Analyst” in the search field.
The resulting data provides a reference number known as the Standard Occupational Code (SOC). In this case, the SOC is 15-1211.00. This code is critical because it is recognized across various federal databases, including the BLS. Many government forms will ask for this SOC code, so it is important to determine the correct one for your specific role early in the process.
Note: Job titles vary significantly from company to company. Always focus on the duties of the occupation to establish the relevant SOC, rather than relying solely on your internal job title.
Analyzing the Job Zone and SVP Range. Once you have the SOC, scroll down to the “Job Zone” section. We look at three key data points here to determine the complexity of the role:
- Education: Does the job require a degree?
- Job Training: How much preparation is needed?
- SVP Range: This indicates the degree of skill required.
In our “Computer Systems Analyst” example:
- Job Training: It indicates that only one to two years of training is required.
- SVP Range: The score is 6.0 to < 7.0.
- Analysis: For high-level EB-1 cases, we typically look for an SVP range of 7.0 to 8.0+. A score below 7.0 suggests the role may not be viewed as “particularly skillful” by immigration standards. Additionally, the education section suggests that only a modest amount of education (perhaps an Associate’s degree) is required.
Example 2: Analyzing Salary Thresholds (Financial Manager)
Now, let’s look at a higher-level role. In the search field, we enter the job title “Financial Manager.”
We find a match with the SOC 11-3031.00.
Assessing Difficulty and Skill When we review the “Job Zone” for Financial Managers:
- Education: A four-year Bachelor’s degree is typically required.
- SVP Range: This role scores between 7.0 and 8.0.
- Analysis: A score of 8.0 denotes a very high level of difficulty. This confirms that “Financial Manager” is a complex, high-skill occupation suitable for EB-1 consideration.
Benchmarking Your Salary
Once the occupation coding and skill level are established, the next step is to review the earnings associated with the position. Remember, our goal is to prove your earnings are above the 90th percentile.
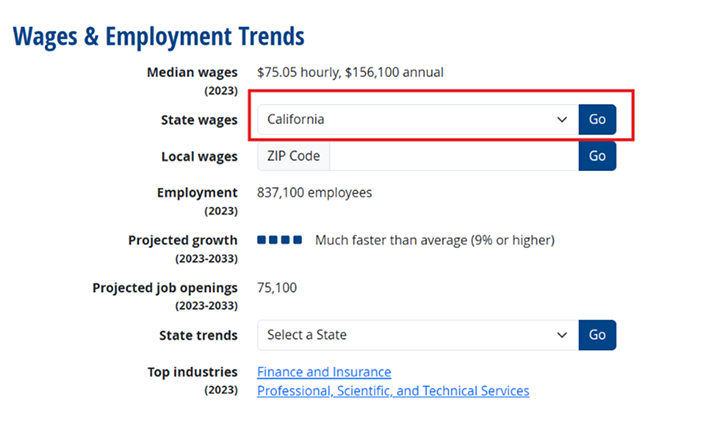
Scroll down to the section titled ‘Wages & Employment Trends’. This section pulls financial data directly from the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
To find the specific salary range for your location, click on the ‘Select a State’ dropdown menu. In this case, we have selected California.
Interpreting the Data: The data will display various earning tiers:
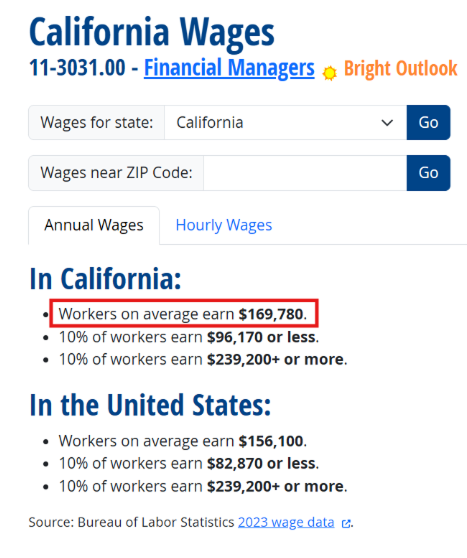
- Median Wage: In California, the median wage for a Financial Manager is $169,780.
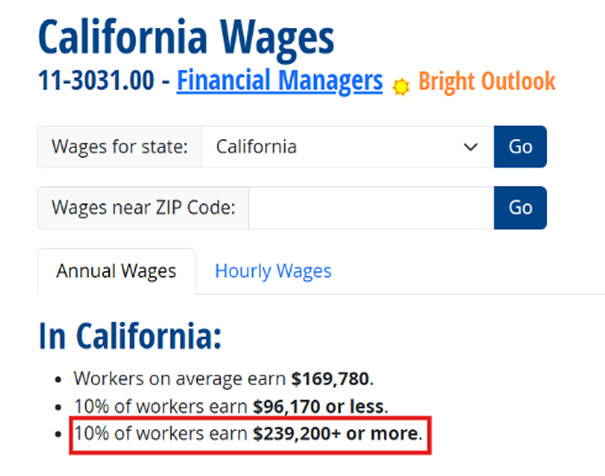
- Top 10% Threshold: To qualify for the EB-1 “High Salary” criterion, you must earn more than the 90th percentile figure.
As shown in the data, the top 10% of Financial Managers in California earn $239,200 or more. Therefore, for EB-1 purposes, you would need to document that your total remuneration equals or exceeds this amount to claim this criterion successfully.
Why High Earnings Matter for Your Green Card
Meeting the high salary requirement does more than just check a box on a form; it serves as objective proof of your extraordinary ability. In the eyes of the USCIS, if the market is willing to pay you significantly more than your peers, it is because you possess a level of expertise that is in scarce supply.
Furthermore, many of our candidates find that their earning potential increases even further once they secure their Green Cards. Permanent residency allows you to compete properly in the open market, unrestricted by employer-specific visas, unlocking new career opportunities and higher compensation.
Act Now: Do You Earn in the Top 10%?
If your analysis on O*NET shows that your salary commands the top tier of your field, you are already on your way to a Green Card. You only need to meet three of the ten criteria to qualify.
Don’t navigate this complex process alone. Contact the Law Offices of Chris M. Ingram today.
Let us help you turn your professional success into permanent U.S. residency.

EB1 – Green Card – Checklist Summary

EB1 – One Time International Award

EB1 – National Awards

EB1 – Invited Memberships

EB1 – Publications About You

EB1 – Participation on Judging Panel

EB1 – Innovation or Invention

EB1 – Published Scholarly Articles

B1 – Exhibitions and Showcases

EB1 – Leading or Critical Roles

EB1 – High Salary or Remuneration

EB1 – Commercial Success in Arts





You must log in to post a comment.